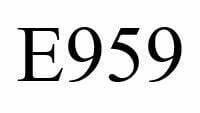What is E 959?
Food additive E 959, Neohesperidine dihydrocalcon DC is a semi-synthetic sweetener with high sweetening power . It is a derivative of natural flavones from the inner layer of the citrus peel, for example narginine (the bitter principle in grapefruit peel), neohesperidine from Seville oranges, and prunine.[i]
How is E 959 additive obtained?
Industrially, the additive E 959 is obtained from narginine (a flavonoid from the peel of citrus fruits) by treating it with alkali, followed by its condensation with isovanillin. The resulting neohesperidinchalcone is hydrogenated in an alkaline medium, resulting in dihydrochalcone neohesperidin (Neo DHC).
Which foods contain the food additive E 959?
According to Regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 the additive E 959 can be used in the following products:
- Flavoured fermented milk products, including heat-treated products;
- Fat and oil emulsions, including spreads,
- Ice cream;
- Fruit and vegetables in vinegar, oil or brine;
- Fruit and vegetables preserved in tins or jars;
- Fruit and vegetable preparations, except compotes;
- Extra jams and extra jellies
- Jams, jellies and marmalades and sweetened chestnut puree as defined;
- Other similar fruit and vegetable spreads;
- Cocoa and chocolate products;
- Other confectionery, including breath freshening drops;
- Decorations, coatings and fillings, except fruit-based fillings;
- Chewing gum;
- Breakfast cereals;
- Fine bakery products;
- Non-heat treated processed meat;
- Heat-treated processed meat;
- Processed fish and fishery products, including molluscs and crustaceans;
- Table-top sweeteners in liquid form;
- Powdered table sweeteners;
- Table-top sweeteners in tablet form;
- Mustard;
- Soups and broths;
- Sauces;
- Salads and spicy spreads;
- Protein products;
- Dietary foods for special medical purposes;
- Dietary foods for weight control, intended to completely replace the daily food intake or an individual meal (in whole or in part the total daily food intake);
- Fruit nectars,
- Flavoured drinks;
- Beer and malt beverages;
- Apple and pear cider;
- Other alcoholic and spirituous beverages containing less than 15% alcohol, including mixtures of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages;
- Potato, cereal, flour or starch-based snacks;
- Processed nuts;
- Desserts;
- Food supplements supplied in solid form, including capsules and tablets and other similar forms, with the exception of chewable forms;
- Food supplements supplied in liquid form;
- Food supplements supplied in syrup or chewable form. [ii]
Are there any side effects from consuming the food additive E 959?
In Europe, the safety of neohesperidin DC was evaluated in 1988 by the Scientific Committee on Food (SCF) of the European Commission – now the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) established by the SCF is 0-5 mg/kg body weight.
Neohesperidine DC is approved for a variety of uses in food, beverages and sweeteners in the EU under Annex II of Regulation 1333/2008.
According to studies, the additive E959 dihydrochalcone neohesperidin does not present any health risk to the consumer.
Toxicological studies carried out on animals showed that the dose of 1 g/kg body weight ingested by them did not produce toxic effects.
Although sugar substitutes are commonly used by people who want to lose weight, there is no clear evidence that sweeteners improve health or help people lose weight. E 959 is currently not recognised as a sweetener in the US. In the US it is used as a flavour enhancer. It is considered harmless!
What are the characteristics of E 959 additive?
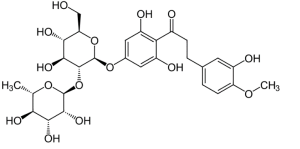
Synonyms of the additive are: hesperidin dihydrochalcone, 4′-β-neohesperidosite, neohesperedin DC.
Its chemical name is 2-o-α-1-ramnopyranosyl-4′-β-D-glucopyranosyl hesperidin, dihydrochalcone.
It has the empirical formula C28 H36 O15 , and the molecular mass M = 612.6.
It occurs as a white crystalline powder and is an odourless substance with a pronounced sweet taste, more persistent than sucrose. Its sweetening power is 1000 times that of sucrose.
An important characteristic of this additive is its high sweetening power (1000 times sweeter than sucrose), but at the same time its instability at acidic pH values (pH ≤ 2) and high temperatures (over 100º C).
The following are the purity characteristics that must be met by the food additive E959.
| Composition | Contains not less than 96% on the dried basis |
| Description | White crystalline powder, odourless. Approximately 1 000-1 800 times sweeter than sucrose |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in hot water, very slightly soluble in cold water, practically insoluble in ether and benzene |
| Maximum ultraviolet absorption | Between 282 and 283 nm for a solution of 2 mg in 100 ml methanol |
| Neu Test | Dissolve approximately 10 mg neohesperidine DC in 1 ml methanol, add 1 ml of 1% methanolic solution of 2-aminoethyl diphenyl borate.
A bright yellow colour appears |
| Loss on drying | Not more than 11% (105º C, 3 hours) |
| Sulphated ash | Not more than 0,2% on a dry matter basis |
| Arsen | Not more than 3 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
| Plumb | Not more than 2 mg/kg expressed on dry weight basis |
The maximum inclusion dose is between 10 and 400 mg/kg.
The maximum acceptable daily intake is 5 mg/kg body weight.[iii]
Why is it useful and necessary to use E959?
The E 959 additive has a special characteristic because, in addition to its use as a sweetener in food formulations, it can also act as a flavour enhancer as well as a masking agent, which makes it different from other alternative sweeteners used in the industry.
– Due to its pleasant and intense sweet taste the additive is accepted in different applications and sectors, always satisfying the end consumer.
– As a flavour enhancer, the flavonoid Neohesperidin DC works by enhancing the flavours of fruit and cocoa derivatives.
– As a masking agent, it reduces unwanted flavours in various food formulations, such as acidity, bitterness, etc.
– It can be used in low concentrations and is one of the natural sweeteners with a higher sweetening intensity.
– The pleasant mouthfeel of Neohesperidin DC lingers longer than other sweeteners, making the intake more enjoyable for the end consumer.
– Neohesperidin DC improves mouthfeel and texture, providing creaminess to various foods.
– Both the caloric intake of Neohesperidin DC and its glycemic index are zero. This advantage allows Neohesperidin DC to be used in more products than other sweeteners, including products for the population suffering from pathologies associated with obesity or metabolic syndrome.
– Its high stability at different temperatures allows Neohesperidin DC to be used in different sectors and at different stages of the production process.
– Its versatility as a sweetener, enhancer or flavour masker using effective amounts on the order of ppm, less than other known sweeteners would require, makes Neohesperidin DC an economical food ingredient.
- Neohesperidin DC has the ability to achieve its desired effects using small amounts of it and also has synergistic effects with other more expensive sweeteners. This allows a smaller amount of the more expensive regular sweetener and a smaller amount of Neohesperidin DC to achieve a similar taste effect for which a larger amount of the regular individual sweetener would be required. [iv]
What are food colours?
Colours are substances that add or restore colour to foods and include natural components of food or other natural substances that are not usually consumed as foods in their own right and are not usually used as characteristic ingredients in food. The category of colours also includes preparations obtained from foodstuffs and other natural edible raw materials obtained by physical and/or chemical extraction leading to a selective extraction of pigments in relation to nutritive or aromatic constituents.[v]
When is the use of food colours acceptable?
The use of food colours is considered acceptable for the following purposes:
- restoring the original appearance of food whose colour has been altered by processing, storage, packaging and distribution;
- improving the visual attractiveness of food products;
- colouring of foodstuffs that are normally colourless.
The use of food colours must always respect the general condition of not misleading the consumer. For example, the use of colours must not give the impression that it contains ingredients that have never been added.[vi]
Conclusions and Legislative Regulations E 959
The E 959 additive, Neohesperidine DC, is approved for a variety of uses in food, beverages and sweeteners in the EU under Annex II of Regulation 1333/2008.
The E 959 additive, Neohesperidin DC is recognised as an economical and stable solution to various challenges in several industry sectors.
Due to its versatility as a food additive, it can be used in different food industries and with different desired effects as follows:
– As a sweetener and to improve taste,
– For its flavour-enhancing power, it is highly valued in sauces and soups, in the animal feed industry and the health industry,
– In the pharmaceutical industry, it is mainly used as a masking agent.
– In personal care products (such as mouthwash, toothpaste) the additive is used because of its sweetening effect.5
Commission Regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council by establishing a Union list of food additives sets out the purity criteria to be met by the food additive E959.
Author: dr.ing. Fulvia Ancuta Manolache
Bibliographical references
[i] Elena Oranescu, Food Additives-necessity and risk, SemnE Publishing House, 2005, Bucharest
[ii] Commission Regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council by establishing a Union list of food additives
[iii] https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2020.e181110
[iv] https://www.bordas-sa.com/en/neohesperidin-dihydrochalcone-the-multi-task-solution/
[v]http://insp.gov.ro/download/cnmrmc/Ghiduri/Igiena%20Alimentatiei%20si%20Nutritiei/Ghid-Aditivi-Alimentari.pdf
[vi] http://www.ansvsa.ro/informatii-pentru-public/sanatate-publica/
8 Photograph 1: https://pixabay.com/ro/photos/prajituri-deserturi-1868573/
9Photo 2: https://pixabay.com/ro/photos/suc-proasp%c4%83t-de-portocale-stors-1614822/